您当前的位置:首页 > 科研进展
[发布日期: 2023-10-18 浏览量 3984]
全球气候模式是一个复杂的系统,用于描述大气、陆地、海洋、海冰及其相互作用,已被广泛应用于研究气候变化及其相关机理。然而,当代模式对地表气温的模拟仍然存在缺陷。过去几十年来,许多研究表明,在大多数模式中,中国区域普遍存在冷偏差,但其相关机制仍不清楚。该模拟不足的根本原因是研究的热点话题。
基于最先进的模式,课题组从地表能量收支的角度研究了中国区域冷偏差的原因。结果表明,由大气状态偏差造成的晴空向下长波辐射的模拟不足是主要原因,而由地表反照率和感热通量变化引起的冷偏差在地区和季节上均存在差异。
The global climate model is a complex system used for describing the atmosphere, land surface, ocean, sea ice components, and their interactions. It has been widely applied to investigate climate change and its associated mechanisms. However, there are still deficiencies in current models for surface air temperature (SAT) simulations. In past decades, many studies have shown prevalent SAT cold biases over China in most models, while the related mechanisms remain unknown. The underlying cause for insufficient simulation is a hot topic of research.
Based on the state-of-the-art models, we investigate the causes of the cold biases over China from the perspective of a surface energy budget. The results indicate that the deficiency of downward clear-sky longwave radiation simulation due to the bias of atmospheric states is the primary reason, and the cold biases induced by surface albedo and sensible heat flux vary among regions and seasons.
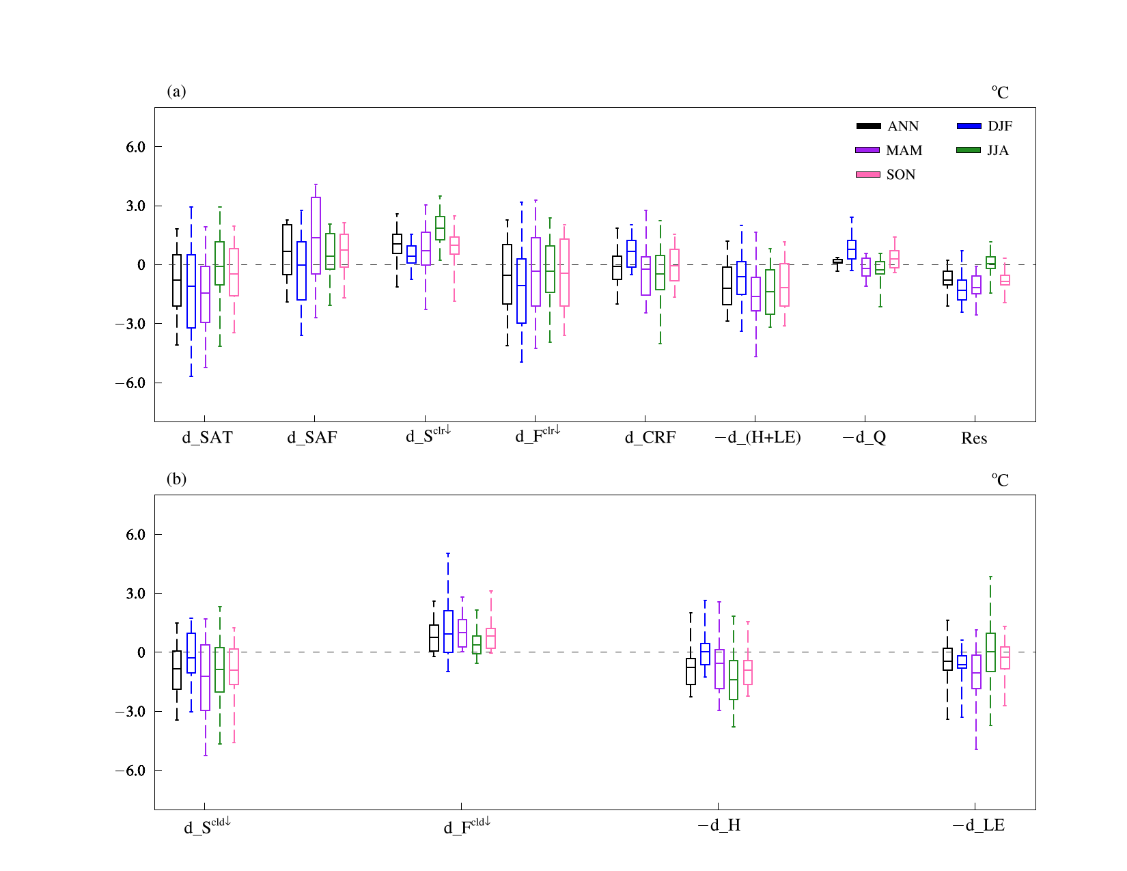
图1 1979−2014年中国区域平均的模式与CN05/再分析之间的地表气温偏差(d_SAT)及相关项(单位:℃)。这些项包括,由地表反照率反馈偏差(d_SAF),晴空地表向下短波(d_Sclr↓)和长波(d_Fclr↓)辐射偏差,地表云辐射强迫偏差(d_CRF),地表热通量偏差[d_(H+LE)],地表储热偏差(d_Q)和残差项偏差(Res)引起的地表气温偏差(d_SAT)。d_CRF可以进一步分解为云短波(d_Scld↓)和长波(d_Fcld↓)强迫偏差,d_(H+LE)包括感热(d_H)和潜热(d_LE)偏差。箱体的顶部和底部分别代表上四分位值(第75百分位)和下四分位值(第25百分位)。箱体外的上/下虚线分别表示31个模式中的最大/小值,箱体的中间线代表多模式集合平均值。黑色、蓝色、紫色、绿色和粉色分别表示年平均、冬季、春季、夏季和秋季的值。
引用格式:
Wang, L., Liu, Z., Lang, X., & Jiang, D. (2023). Understanding surface air temperature cold bias over China in CMIP6 models. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 128, e2023JD039515.