您当前的位置:首页 > 科研进展
[发布日期: 2024-03-19 浏览量 4676]
【中文介绍】
青藏高原热源对于中国、东亚乃至整个北半球的气候系统具有深远的影响。过去的研究主要侧重于中低纬度地区对高原热源的影响,但对于高纬度地区信号的研究相对较少。因此,本研究以ERA5再分析数据为基础,系统分析了欧亚北部冬季积雪对初夏高原大气热源的影响及其机制。
综上所述,本研究揭示了欧亚北部冬季积雪对初夏高原大气热源的影响及其机制,为深入理解青藏高原热源的影响因素及其对全球气候的影响提供了新的视角。
【英文介绍】
The Atmospheric heat source of the Tibetan Plateau (TPHS) exerts a profound influence on the climate system of China, East Asia, and even the entire Northern Hemisphere. Previous research has primarily focused on the impact of mid- and low-latitude regions on TPHS, with relatively limited investigations conducted in high-latitude areas. Therefore, utilizing ERA5 reanalysis data, this study comprehensively examines the effects and mechanisms of winter snow in northern Eurasia TPHS during early summer.
The findings demonstrate that excessive winter snow in northern Eurasia facilitates the process of snowmelt and enhances soil moisture during early summer. This rise in humidity further amplifies the cooling effect on the upper atmosphere, thereby intensifying the meridional temperature gradient between north and south Eurasia. The enhanced temperature gradient further reinforces the mid-latitude westerly jet, thereby augmenting near-surface wind speed and intensifying sensible heat flux over the TP. Moreover, the intensified meridional temperature gradient induces anticyclones and high-pressure anomalies on the southwest side of the TP, leading to reduced precipitation and latent heat release. Considering that latent heat dominates the TPHS in early summer, excess winter snow in northern Eurasia will eventually weaken TPHS in early summer, with local soil moisture playing a pivotal role in this process.
In summary, this study reveals the impact and mechanism of northern Eurasian winter snow on TPHS in early summer and provides a new perspective for a deeper understanding of the influencing factors of TPHS and its impact on global climate.
【关键图表】
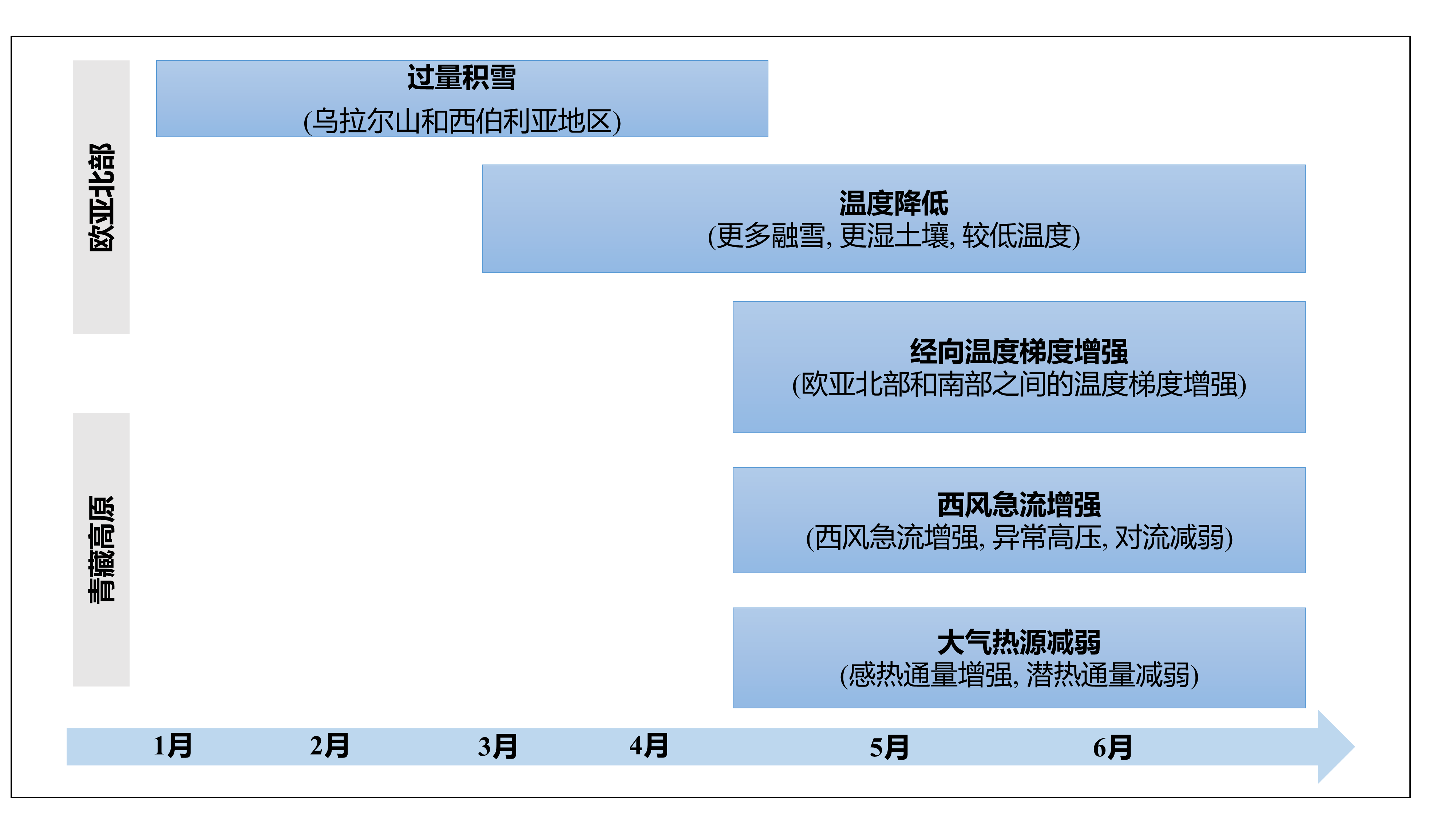
图:欧亚冬季积雪影响高原初夏大气热源的流程图
【引用格式】
Han, Y., Jiang, D., Si, D. et al. Influence of winter northern Eurasian snow depth on the early summer Tibetan Plateau heat source during 1950–2019. Clim Dyn (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-024-07130-4